What is a Lithium-ion Battery?
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are rechargeable energy storage devices that have become the most prevalent battery technology in portable electronics and electric vehicles. They operate based on the reversible intercalation of lithium ions between the anode and cathode during charging and discharging cycles. The first commercial Li-ion battery was introduced in 1991, marking a significant advancement in battery technology, which has since evolved to provide higher energy densities, longer cycle lives, and reduced costs over time.
The structure of a Li-ion battery typically consists of:
- Anode: Usually made from graphite, where lithium ions are stored during charging.
- Cathode: Commonly composed of lithium cobalt oxide or other lithium compounds.
- Electrolyte: A liquid or gel that facilitates the movement of lithium ions between the anode and cathode.
- Separator: A porous material that prevents direct contact between the anode and cathode while allowing ion transfer.
Li-ion batteries are characterized by their high energy density (up to 330 Wh/kg), low self-discharge rate, and ability to deliver high power outputs, making them suitable for applications ranging from consumer electronics to electric vehicles and grid storage.
What is a LiFePO4 Battery?
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries represent a specific type of lithium-ion battery that utilizes lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material. This chemistry offers distinct advantages, including enhanced thermal stability, safety, and a longer cycle life compared to traditional Li-ion batteries. LiFePO4 batteries were developed in the early 1990s but gained popularity in the 2000s due to their improved safety profile and performance in high-drain applications.
Key features of LiFePO4 batteries include:
- Safety: They are less prone to overheating and thermal runaway compared to other Li-ion chemistries.
- Cycle Life: Typically can endure more charge/discharge cycles (up to 2000 cycles) without significant capacity loss.
- Energy Density: While generally lower than traditional Li-ion batteries (about 90-120 Wh/kg), their stability makes them ideal for specific applications.
LiFePO4 batteries are commonly used in electric vehicles, solar energy storage systems, and applications requiring robust performance under varying conditions.
Similarities Between Lithium-ion and LiFePO4 Batteries
The working principle of both batteries is similar. The lithium ions in the battery move between the positive and negative electrodes for discharge and charge. Secondly, both batteries are rechargeable. And they both use graphite carbon electrodes and metal backing as anodes.
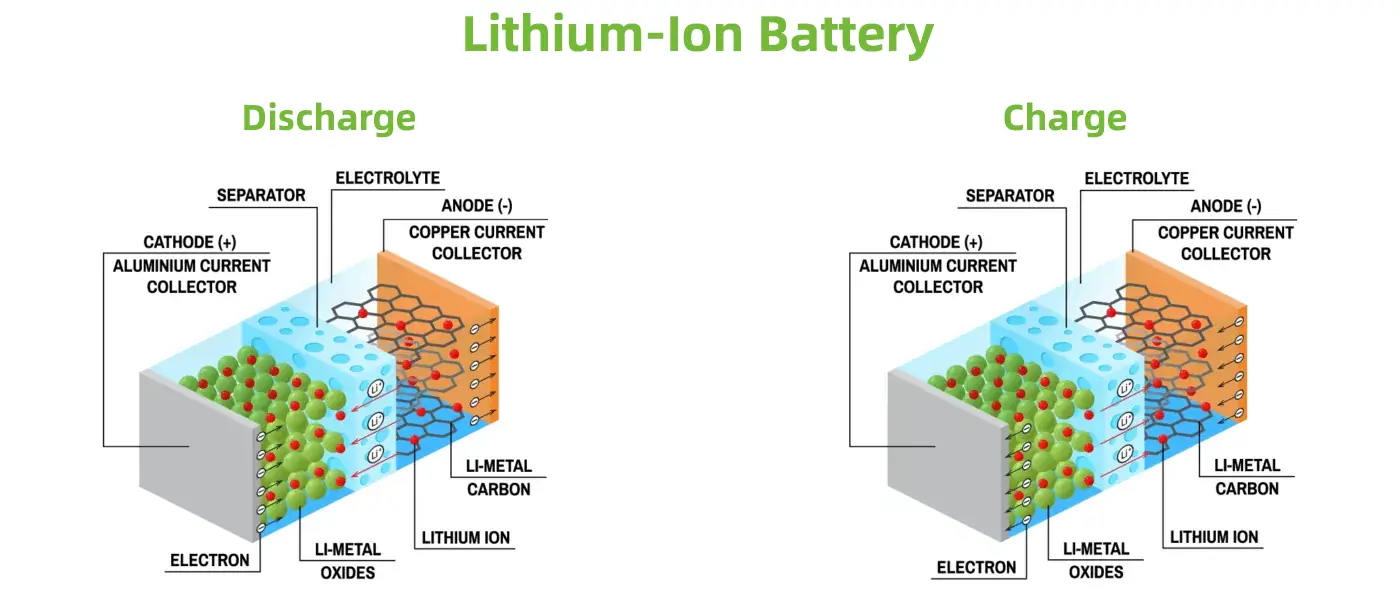
Differences Between the Two
|
Feature
|
Lithium-ion Battery
|
LiFePO4 Battery
|
|
Energy Density
|
Higher (up to 330 Wh/kg)
|
Lower (90-120 Wh/kg)
|
|
Cycle Life
|
Moderate (500-1500 cycles)
|
High (up to 2000 cycles)
|
|
Thermal Stability
|
Moderate
|
High
|
|
Safety
|
Risk of thermal runaway
|
Very safe; lower risk
|
|
Cost
|
Generally lower
|
Higher due to raw materials
|
|
Weight
|
Lighter
|
Heavier
|
Which one is better, lithium-ion battery or lithium iron phosphate battery?
When comparing lithium-ion batteries and lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries, both technologies have their unique advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different applications. Here’s a breakdown of their characteristics to determine which might be better for specific needs.
Advantages of Lithium-ion Batteries
- Higher Energy Density: Lithium-ion batteries typically have a higher energy density (around 150-200 Wh/kg) compared to LiFePO4 batteries (90-120 Wh/kg). This makes them ideal for applications where space and weight are critical, such as in smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles that require longer ranges.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Generally, lithium-ion batteries are less expensive upfront than LiFePO4 batteries, making them a more attractive option for consumer electronics and applications where cost is a significant factor.
- Widespread Availability: Lithium-ion technology is well-established and widely used across various industries, leading to a broader range of products and support options available in the market.
Advantages of Lithium Iron Phosphate Batteries
- Safety: LiFePO4 batteries are known for their excellent thermal stability and safety profile. They are less prone to overheating and thermal runaway, making them safer for applications where safety is paramount, such as electric buses and stationary energy storage systems.
- Long Cycle Life: These batteries can endure a significantly higher number of charge-discharge cycles (1,000 to 10,000 cycles) compared to lithium-ion batteries (500 to 1,500 cycles). This longevity translates into lower long-term costs due to fewer replacements needed over time.
- Environmental Friendliness: LiFePO4 batteries do not contain toxic heavy metals like cobalt, making them more environmentally sustainable. The materials used are abundant and pose fewer ethical concerns regarding sourcing.
- Performance in Extreme Conditions: LiFePO4 batteries perform well in high-temperature environments and have a lower risk of failure under stress or extreme conditions. This makes them suitable for applications in harsh climates or demanding operational settings.
Which is Better?
The choice between lithium-ion and lithium iron phosphate batteries largely depends on the specific application requirements:
- Choose Lithium-ion Batteries if you need:
- Higher energy density for compact devices.
- A lower initial cost for consumer electronics.
- Lightweight solutions for portable applications.
- Choose Lithium Iron Phosphate Batteries if you need:
- Enhanced safety features for high-risk applications.
- Longer lifespan with fewer replacements.
- Environmentally friendly options with stable performance in extreme conditions.
In summary, neither battery type is universally "better"; instead, the decision should be based on the specific needs of the application, including factors like safety, cost, space constraints, and environmental conditions.
When to Use Lithium-ion Batteries for Home Storage?

Lithium-ion batteries, particularly those with nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) chemistry, are a good choice for home storage in the following scenarios:
- When space is limited: Li-ion batteries have a higher energy density, allowing more storage capacity in a smaller footprint.
- For occasional backup power: Li-ion batteries can provide reliable backup power during outages without the need for daily cycling.
- When cost is a major factor: NMC Li-ion batteries tend to be more affordable than LFP alternatives.
However, Li-ion batteries have some drawbacks for home storage, such as:
- Narrower operating temperature range: Li-ion batteries function best between 32°F (0°C) to 113°F (45°C), requiring climate-controlled storage.
- Higher risk of thermal runaway and fire: Li-ion batteries, especially those with NMC chemistry, are more prone to overheating and fire hazards.
When to Use Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) Batteries for Home Storage?
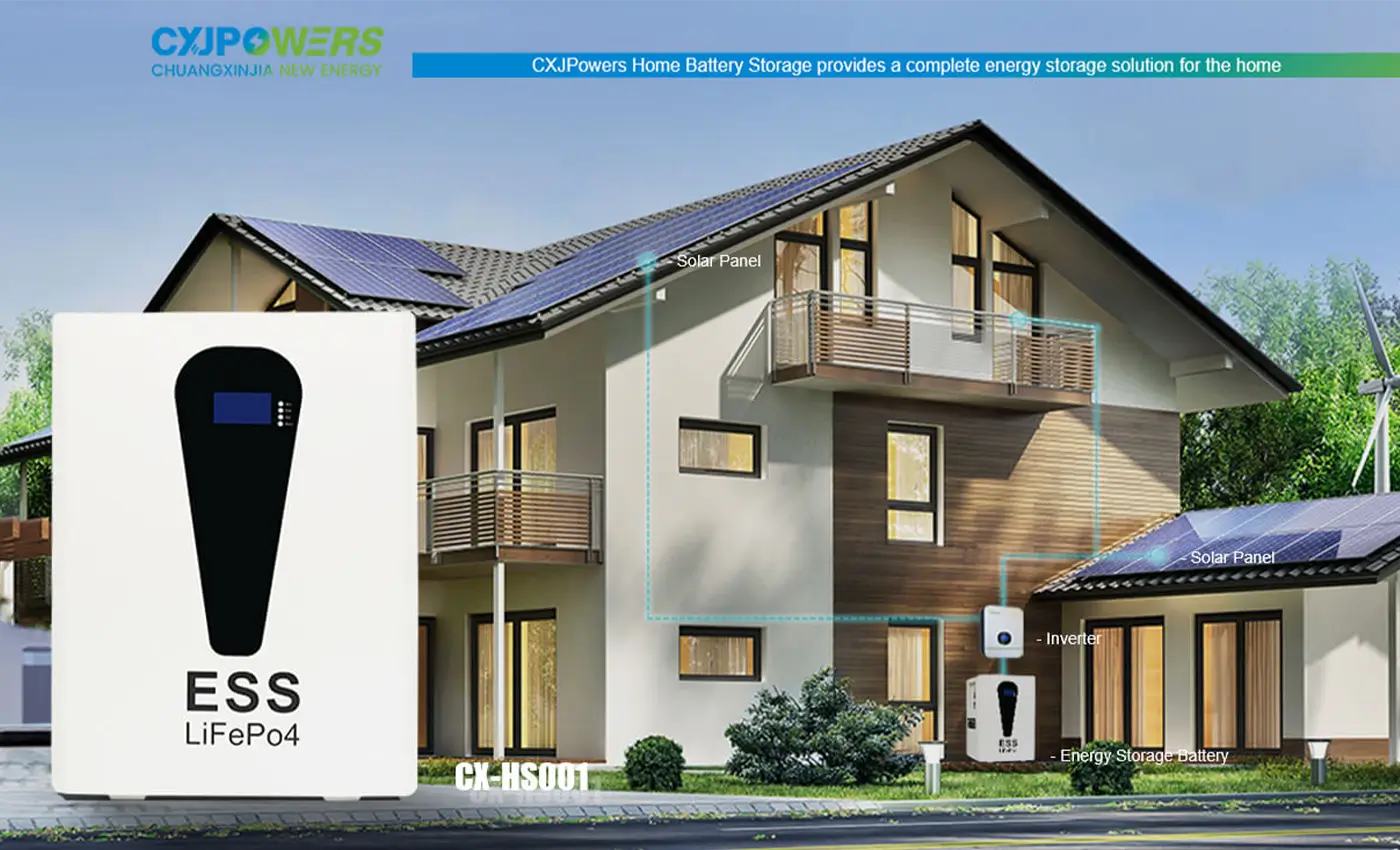

Lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries are ideal for home storage in the following situations:
- When safety is the top priority: LFP batteries have a very low risk of thermal runaway and are less likely to catch fire, making them safer for home use.
- For daily cycling and off-grid applications: LFP batteries can withstand thousands of charge/discharge cycles, making them suitable for frequent use in solar and off-grid systems.
- In harsh environments: LFP batteries can operate in a wider temperature range of -4°F (-20°C) to 140°F (60°C), allowing for more flexible installation locations.
The main drawbacks of LFP batteries are:
- Higher initial cost: LFP batteries tend to be more expensive than NMC Li-ion alternatives.
- Lower energy density: LFP batteries have a lower energy density, requiring more space for the same storage capacity.
In summary, lithium-ion batteries are a good choice for occasional backup power in space-constrained homes, while LFP batteries are ideal for daily cycling, off-grid use, and safety-critical applications. The choice ultimately depends on the specific needs and priorities of the homeowner.

-------------------
Welcome to customize lithium home battery. Contact us for details!




